The process of growing onions has a number of features and consists of several important stages, the strict observance of which will allow you to get a good harvest of fruits. In this article, we will consider the rules for selecting and preparing a site for growing onions, recommendations for preparing and planting planting material, especially for caring for plants and combating possible diseases or pests, and also list the best varieties of onions for growing in open ground.
The best varieties for planting
There are many different varieties of onions, which differ from each other in terms of ripening, the taste of the fruits and their appearance. But experienced gardeners have chosen some of the best varieties of onions, which have proven themselves when grown at home.
Did you know? In ancient Greece, the bulb was considered a symbol of the universe and gave the heads of vegetables to oracles and priests.
Consider a brief description of the best varieties:
- Kaba. Harvest ripens in 110-120 days. The bulbs are round, covered with a golden husk from the outside, and their mass reaches 145 g. The pulp is white and juicy, has a moderately sharp taste. This variety is poorly stored, but can be used for conservation.

- Red baron. The variety ripens in 95-110 days. The fruits are large, have a round shape, slightly flattened above and below. The color of the flakes is purple or dark red. Bulb weight can reach 150 g. The pulp of the fruit is dark red or purple, juicy, and the taste is semi-sharp. Onions of this variety are well stored; fresh salads and various canned preparations can be prepared from it.

- Snowball. Ripening of fruits occurs after 90-100 days from the time of planting. The bulbs are covered with white husk and have a round shape. The mass of one fruit is from 120 to 200 g. The pulp is white, the taste is semi-sharp. The fruits are well stored, it is recommended to use them only in fresh form.

- Strigunovsky local. Matures in just 3 months. Bulbs have a round shape and medium size, the mass of one fruit is 45-80 g. Outside, the vegetables are covered with a light brown husk. Their flesh is dense, painted in a light color and has a very pungent taste. This variety is perfectly stored and can be used both fresh and for canning.
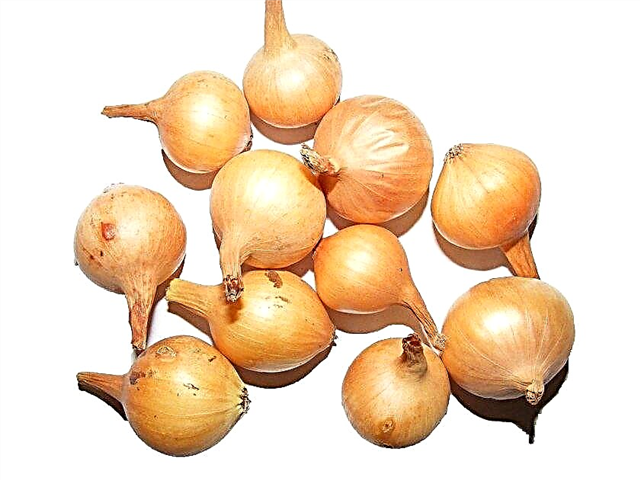

- Sturon. Fruits ripen in 110 days. The bulbs have a round shape, the mass of each of them is 70-180 g. The pulp has a very sharp taste and white color, the outside is covered with yellow-brown scales. Vegetables tolerate storage well and can be used both fresh and for the preparation of canned preparations.
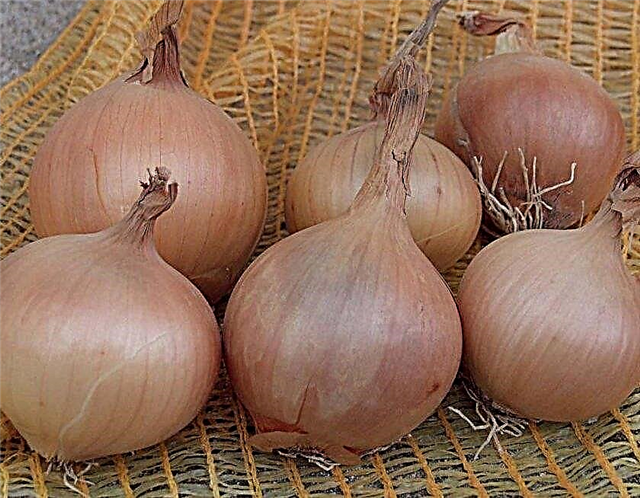

- Texas yellow. Harvest can be harvested after about 90-100 days. The fruits are round and large, covered with light golden peel from the outside. Bulb weight is 80-150 g. The pulp of the fruit is dense, with a rich white color and a semi-sharp taste. Bulbs are characterized by medium keeping quality, it is recommended to use them only in fresh form.
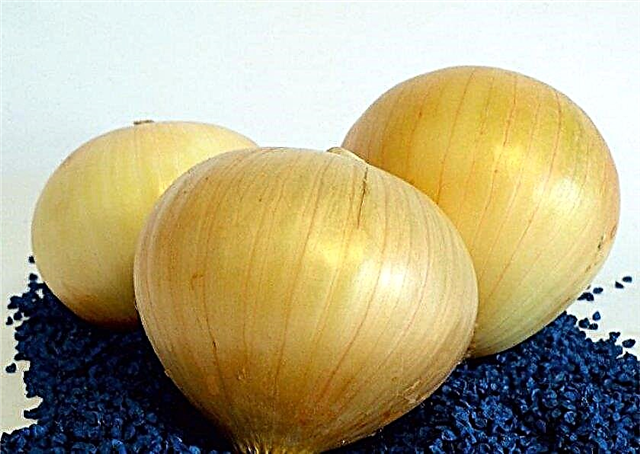

- Centurion F1. Harvest can be harvested after 90 days. The mass of one bulb is 65-150 g. The fruits have a rounded-elongated shape, the outside is covered with a light brown peel. The pulp is juicy, has a white color and a sharp taste. Fruits perfectly tolerate storage and are used fresh or for preservation.

Selection of a place and arrangement of a bed
To collect a generous onion crop, you need to find a suitable place for it on the site.
The main recommendations for the selection and arrangement of beds for onions are listed below:
- the site should be well lit by the sun;
- it is best to plant this crop where cucumbers, potatoes, carrots or legumes were grown last year;
- it is not recommended to plant onions for two years in a row on the same site;
- next to the onion beds you can plant zucchini, herbs or carrots;
- the site should be located on a hill in order to avoid flooding by rain or melt water;
- when forming ridges for onions, their height should be 12-15 cm, and their width should not exceed 1 m;
- Before planting the planting surface, the surface of the ridge must be leveled with a rake.
Important! When planting onions, it is recommended to place rows from north to south so that the soil around the plants is better warmed up by the sun.
Land preparation for planting
Onions grow best in moderately moist, loose and fertile soil, which allows air and water to pass through well. Depending on the planting dates, planned spring and autumn tillage is carried out. Consider its main features in more detail.
Demanding culture to the composition and structure of the soil
Onions have weak roots, so they need loose and light soil. If the soil on the site is too heavy, it is recommended to form small raised ridges before planting the onion. This is necessary so that the earth is better warmed up by the sun, does not accumulate too much moisture and passes air well.

To get a good crop, you need to plant onions in fertile soil so that plants receive all the nutrients necessary for growth. But even in this case, it is necessary to additionally fertilize so that the bulbs are large and have a good taste.
Features of different types of soils and their preparation
It is best to plant onions in fertile and loose chernozem. But this type of soil is quite rare, so you can plant sowing and other types of soil. In this case, you need to know what to add to them to increase fertility.
Did you know? In ancient Rome, only poor people ate onions. The rich did not like the bitter taste and specific aroma of the vegetable, so they believed that eating it was indecent.
Depending on the type of soil, such ingredients are added to it (the amount is indicated per 1 m² of area):
- loamy soil has a suitable structure for growing vegetables, but needs to be enriched with nutrients, so 4 kg of humus and peat, 1 tsp. urea and 2 tbsp. superphosphate;
- clay soil is too heavy for a weak root system of onions, so it is mixed with peat and humus (6 kg each), 1 tsp of urea and 1 tbsp are added. superphosphate and nitrophosphate;
- in loose and light peat soil add 5 kg of humus or compost, 1 part of urea and 1 tbsp. superphosphate and nitrophosphate to enrich it with essential nutrients;
- sandy soil is poor in useful components, so it is best suited for growing onions. In it add 1 bucket of peat, humus and compost, 2 buckets of clay, 2 tbsp. superphosphate and 1 tbsp. nitrophoski, and after digging make 2 liters of liquid potash fertilizers.
Technology of autumn and spring tillage for planting
The procedure for preparing soil for planting onions is carried out in autumn and spring in order to enrich the soil with useful substances and destroy pathogens and larvae of pests.

The basic rules for autumn tillage for planting winter onions are listed below:
- Autumn soil preparation begins after harvesting;
- you need to collect and destroy all plant debris, because larvae and pupae of pests may remain on them;
- for disinfection, it is recommended to water the soil with a solution of copper sulfate;
- humus and fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium are added to the soil. Throughout the winter they are evenly distributed in the soil;
- the land on the site needs to be dug to a depth of about 20 cm;
- the surface of the excavated area is not leveled so that all pathogens and pests die under the influence of low air temperature.
Important! To keep the soil loose and speed up its heating, the prepared bed for planting onions is covered with a film and left for a week.
Spring tillage is carried out according to the following rules:
- make organic and mineral fertilizers depending on the composition of the soil. The rules for their introduction were discussed above;
- dig the soil again to additionally saturate it with oxygen;
- a few days before planting, it is necessary to carry out harrowing and loosening of the soil in order to eliminate large lumps and accelerate the evaporation of excess moisture.
Landing technology
When planting onions, it is important to choose the correct timing for planting the planting material so that the sprouts appear at the right time and do not die under the influence of low temperature.

Planting a vegetable can be done in several ways:
- seed planting - It is carried out in the spring, and by the end of summer, onion sets grow out of them. It is used for planting the following year;
- planting sevka - carried out in spring, summer or late autumn in order to obtain onions on a feather or for growing uterine bulbs;
- uterine bulb planting - carried out in the spring in order to obtain seeds.
Did you know? The famous king of England Richard the Lionheart carried a small bulb with him as an amulet to attract good luck in battles.
Spring, Autumn and Summer
Onions can be planted in spring, summer or autumn, depending on when you need to get the crop.

Consider the rules for determining the timing of onion planting, depending on the season:
- spring sowing is carried out from the second half of April to mid-May, depending on the climatic conditions of the region;
- plant spring onions only after the soil temperature has reached + 12 ° C and above;
- during summer planting, sowing is planted in the second half of July to ensure a harvest of fresh greenery until late autumn;
- in the fall, sowing is planted in open ground in the second half of October so that it can take root, but cannot germinate before the onset of cold weather;
- winter onion sowing is carried out a month before the onset of the first frost at an air temperature of at least + 5 ° C.
Preparation and disembarkation
Before planting a seed, it must be prepared and a special treatment should be carried out. This procedure will help planting material take root faster in the soil, accelerate the emergence of seedlings and protect plants from attack by pests.

The list of actions for preparing sowing for planting in open ground is presented below:
- Sort sevka by size. Bulbs with a diameter of 1 to 3 cm are suitable for spring and summer planting, as they sprout faster. For winter planting, a sowing with a diameter of less than 1 cm is used so that it does not have time to grow to frost.
- 10-14 days before planting, planting material must be rearranged in a well-lit and warm place, spreading it with a thin layer on a flat surface. This will help speed up the process of root formation.
- You can fold the sevka into a mesh bag and put it near the battery for 8-10 hours, so that the bulbs warm up well and begin to germinate.
- If planting is carried out in spring and summer, then you need to cut the top dry ponytails to white pulp in order to accelerate the appearance of green shoots. During autumn planting, this procedure is not carried out, because green leaves will die from frost.
- Soak the sevoc in a bowl of warm water for 24 hours. This will saturate the planting material with a sufficient amount of moisture and accelerate its rooting in cold soil in the fall or in insufficiently moist soil during spring and summer planting.
- Then the seed must be placed for 20 minutes in a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect planting material and prevent the appearance of diseases or pests. After processing, the bulbs are rinsed in clean water and allowed to dry slightly.
Depending on the purpose for which this crop is grown, a particular planting scheme is chosen. If you plan to use the green part of plants, then you can plant sowing with a higher density in order to further thin out the rows and pull out part of the young shoots. When growing crops in order to obtain large bulbs, plants are planted at a certain distance from each other to provide them with enough space for the development of a large underground part.
Step-by-step landing instructions
Planting seedlings in open ground is very simple and does not require special skills, so even a beginner gardener will cope with it.

The principle of onion planting does not depend on the time of year and is carried out according to the following rules:
- Make long furrows in the soil at a distance of 30-35 cm from each other. Pour a small amount of warm water on each furrow.
- Place the sowing in the furrow so that between the two neighboring plants there is a distance of at least 10 cm. The bulbs are located bottom to bottom.
- Sprinkle planting material with a small amount of earth and slightly level it with your hands. If the soil is dry, you can slightly water the beds with warm water.
- If the planting is carried out in late autumn, then the beds with planted seedlings are mulched with dry straw and fallen leaves.
Important! It is not recommended to cover the bed with a planted onion film, as seedlings may flutter under it.
Sevk care
In fertile soil, planting material sprouts very quickly, but to get a good crop, you need to provide the plants with proper care. It consists in regular watering, proper care of the soil around the plants and timely application of necessary fertilizers. Let's consider all these components of care for sevk in more detail.
Watering and cultivating
For normal growth, plants need moisture, but with excessive water, the root of the onion can rot. Therefore, the soil on the beds should be moderately moist and loose enough so that the water does not stagnate around the roots.

The basic rules for watering plants are listed below:
- in May, watering is carried out once every 7 days, spending about 6-10 liters of water per 1 m²;
- in June, during the active growth of green mass, 10-12 liters of water are consumed per 1 m², and the frequency of irrigation is 1 time in 8-10 days;
- in July, watering is reduced using 5-8 liters of water for irrigation of 1 m² of beds every 8-10 days. If the weather is too hot, it is permissible to water the onion a little more often;
- in August, irrigation is not carried out so that the formed bulbs can ripen in the ground;
- It is recommended to use the drip irrigation method from a small watering can to moisten the green part of the plants, but not to break it.
Did you know? The scientific name for the onion is Allium. It comes from the Celtic word “all” and translates as “burning”.
So that the weeds do not interfere with the growth of onions, they must be removed immediately after emergence. Weed spacing must be done carefully, as when pulling out large weeds, the bulbs can shift in the ground and slow down growth. If the topsoil is too compacted, carefully loosen it to a depth of 2-3 cm. All these procedures are recommended to be carried out after watering the plants.
Top dressing
In addition to watering and caring for the soil in beds with onions, plants also need a lot of nutrients. Therefore, to obtain a plentiful harvest, know how to fertilize plants and how often to top dress.

The basic rules for applying fertilizers for growing onions are listed below:
- you can use store-bought fertilizers as top dressing, diluting them with the amount of water indicated on the package;
- after the height of the green shoots reaches 5-6 cm, nitrogen-containing and potassium fertilizers are applied with an interval of 10 days;
- during the formation of the bulb make a solution of special complex fertilizers for bulb plants.The interval for making such top dressing is every 12-14 days;
- an aqueous solution of fertilizer is applied by drip irrigation, for which you can use a small watering can;
- the last time fertilizers are applied a month before the planned harvest.
Preparation for cleaning
2-3 weeks before the planned harvest stop fertilizer application. During this period, the green part of the onion gradually begins to dry out, and the application of top dressing can again stimulate unnecessary growth of greenery. Watering the beds before harvesting is also not worth it, because during this period, the plant no longer grows, and waterlogging of the soil can provoke the appearance of rot or fungal diseases, especially in combination with cool air temperature at night.
Harvesting and storage
Depending on the timing of planting and onion varieties, harvesting is carried out in the period from mid-July to early September. The main sign that the crop has ripened is the yellowing of the leaves and their contact with the ground.

Consider the rules for harvesting and storage of harvested onions:
- dig the onion with a pitchfork, and then pull it out of the ground, holding it by the ground part;
- then the onions are laid out in a well-lit place with a thin layer to dry for 2 weeks;
- after drying, dry leaves are removed at a distance of 3-4 cm from the head and leave the onions in a warm place for another 3-5 days. You can decompose it near heating appliances to maintain an air temperature of about +30 ... + 35 ° C;
- dried onions can be braided or bundled in small baskets. Harvest stored in a dry room with a temperature of +5 ... + 20 ° C and good ventilation.
Possible growing problems
With proper care for planting onions, you can avoid the appearance of diseases and pests. But if it was not possible to avoid infection, then you need to be able to determine the type of problem and immediately take the necessary steps to eliminate it.
Important! In the fight against pests and onion diseases, it is not recommended to use chemicals, because they accumulate in the greenery of plants and can be harmful to the human body.
The main onion pests include:
- Tobacco thrips. Insects are very small (about 1 mm) and have a brown body. They lay eggs on the leaves, of which after 3-5 days white larvae appear. The pest sucks the juice from the leaves, so they become yellow and lethargic, the plant lags in growth and begins to decay. To combat thrips, a solution of 1 liter of water, 2 heads of garlic, 0.5 cups of vegetable oil and a teaspoon of liquid soap is used.

- Onion fly. The insect is similar to an ordinary fly, has a gray trunk about 1 cm long. In the second half of May, the insect lays eggs on the leaves of the onion or in the upper soil layer, from which white caterpillars appear in a week. They damage the bulb located in the ground, as a result of which the plant growth stops, the leaves turn yellow, and the onion heads become soft and begin to rot. Affected plants are watered with a tobacco solution prepared from 12 liters of water, 200 g of tobacco, a tablespoon of liquid soap and a pinch of ground hot pepper.
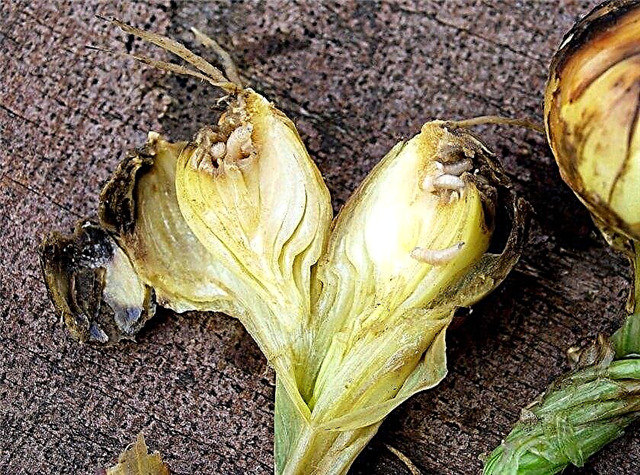

- Stem nematode. The pest is small (up to 1.5 mm) threadlike caterpillars that lay eggs inside the pulp of the bulb. Hatched larvae, as well as adult individuals, feed on the flesh of the head. Signs of a nematode lesion are cracking of the surface of the bulb, its loose structure and slowing plant growth. To control the pest, marigold and marigolds are planted near the beds with onions, and after irrigation, aisles are sprinkled with a mixture of hot pepper and mustard powder.
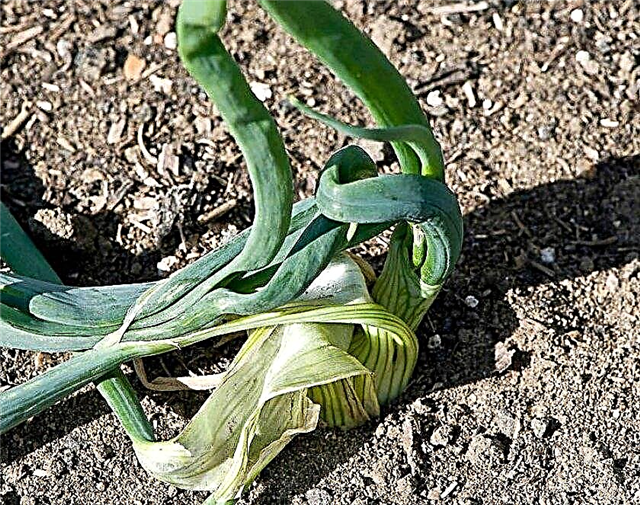

- Onion moth. Butterflies have a body length of about 8 mm and lay yellow eggs on the surface of onion leaves, from which yellow-green larvae appear. Caterpillars live inside the pulp of the leaves and feed on their sap. Affected plants become covered with bright longitudinal spots of irregular shape and begin to turn yellow at the edges. To combat the pest, the beds are sprayed with a cooled broth of 4 kg of tomato tops and 10 l of water.
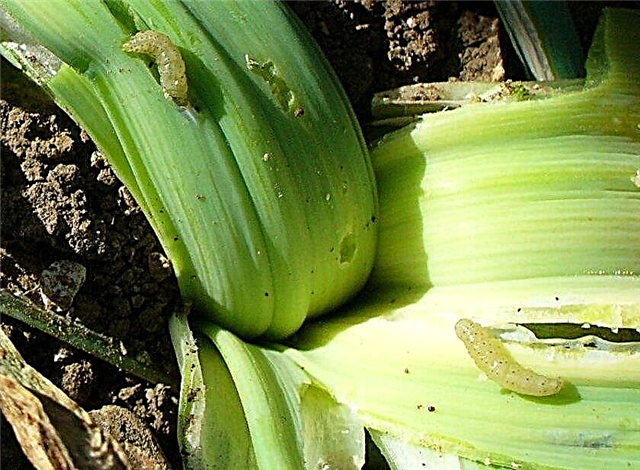

- Root tick. The pest lives inside the bulb and has dimensions of about 1.1 mm. The female lays eggs in the pulp of the onion head, of which caterpillars appear after 2 weeks. They damage the root part of the plant, as a result of which its growth stops, and the surface of the bulb is deformed, becomes rotten and brown. For treatment, diseased plants are watered under the root with a solution prepared from 1 kg of nettle leaves and 5 l of water and diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.

Did you know? Onions are good for the human body, but poisonous for cats and dogs.
The most common onion diseases include:
- Peronosporosis (downy mildew). The disease is fungal and affects plants during wet and warm weather. The source of infection may be contaminated soil or last year's plant debris. Signs of the disease include pale green spots on the leaves of onions, which are subsequently covered with a purple coating. The tops of the leaves turn yellow and dry. For treatment, you need to stop watering the onion and not to make nitrogen fertilizers. With large scale infections, fungicides are used.
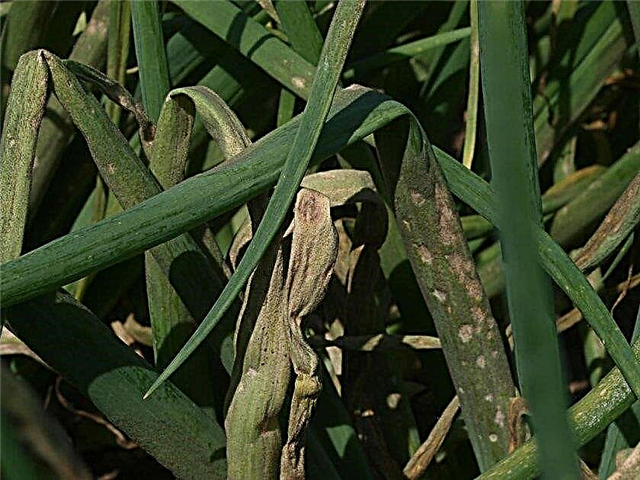

- Onion rust. The causative agent of the infection is a fungus that can winter in the soil on last year's plant debris. Light yellow convex formations appear on the leaves of the affected plants, which eventually change color to black. For treatment, the onions are sprayed with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid.

- Fusarium. This disease has a fungal nature and affects the root of the plant. The roots and the bottom of the bulb become pink and soft, and then die. Brown spots appear on the leaves, and the plant stops growing. Sick specimens need to be removed from the garden bed and destroyed, and then treated onion beds with a fungicide solution.

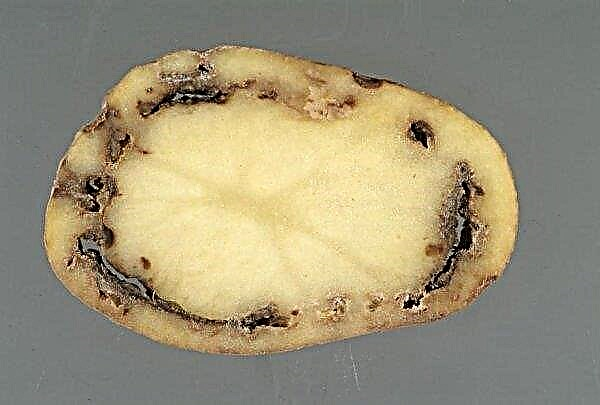
- Bacterial rot. The source of this disease are insect pests that live and breed in onions. The infection affects the heads of the fruits, as a result of which dark sections appear between the layers of the pulp, which eventually decay. Signs of infection are yellowing of leaves and drying of the ground part of the plant. This disease cannot be cured, but can be prevented if the soil is decontaminated with a solution of copper sulfate.

In order to collect a good crop of onions from the beds, you need to correctly select the appropriate variety, choose the right planting dates and carry out the necessary plant care. The recommendations listed in this article will help grow large onions with a good presentation and excellent taste, as well as properly preserve it for the winter.