For residents of Russia, cedar is nothing but a Siberian pine (it is also cedar and Siberian cedar). But in reality, these are different plants — evergreen trees from the Pine family. Pine nuts grow on the Siberian pine, and it is called cedar because of its resemblance. It is useful to find out exactly where the fruits grow, in which zone, and also why they are not in Belarus.
Where pine nuts grow in Russia
Siberian pine is a sought-after species that grows in the taiga, mountains and bolted in the wild. It grows abundantly in the northern part of China (the main variety is Chinese white, or Pinus Armandii), Afghanistan (the most popular Pinus Bungeana), in Mongolia. In Europe, the crop is mainly harvested from Swiss and stone (Pinus Pinea) pines, and in Asia, from Chilgoza Pine (grows in the Himalayas) and Pinus Koraiensis (can be seen in Korea). It grows in Russian territories in large numbers, and often it is dwarf pine and cedar pine.
Important! What the Russians are accustomed to call pine nuts in reality has nothing to do with cedar, since its seeds are inedible. And they eat Siberian pine nuts, including shells, butter, milk, and even flour from such fruits.
The main growing areas of pine nuts collected from cedar pine (the name is figurative, since there is no direct relationship to real cedar) in Russia are as follows:
- Karelia.
- Crimea.
- Siberia, mostly Western.
- The city of Anapa.
- Urals (west of the mountains and up to the Timan Ridge).
- Sverdlovsk, Vologda, Arkhangelsk and Moscow regions, Moscow region, less often Kostroma region.
 Cedar pine fruits after 20 years of growth. Ripening fruits takes 2 years, but they have a unique composition rich in healthy minerals, proteins, amino acids, fats, trace elements and vitamins.
Cedar pine fruits after 20 years of growth. Ripening fruits takes 2 years, but they have a unique composition rich in healthy minerals, proteins, amino acids, fats, trace elements and vitamins.
Important! In almost all species of pines, the standard duration of seed ripening. From the moment the cones form — 2 years.
It is useful to know that different species of pines have their own habitat in Russia, namely:
- Korean pine. Its original homeland is Japan, and in the Russian Federation the plant is found in the Far East, in particular, in the Amur region, Primorye, in the Khabarovsk Territory. The height is up to 60 m. The shoots are quite large, modified. One tree can give up to 500 cones, of which about 150 pieces will have excellent occupancy. Seeding occurs every 4 years, but in the wild, the plant fully produces bumps every 10-15 years.
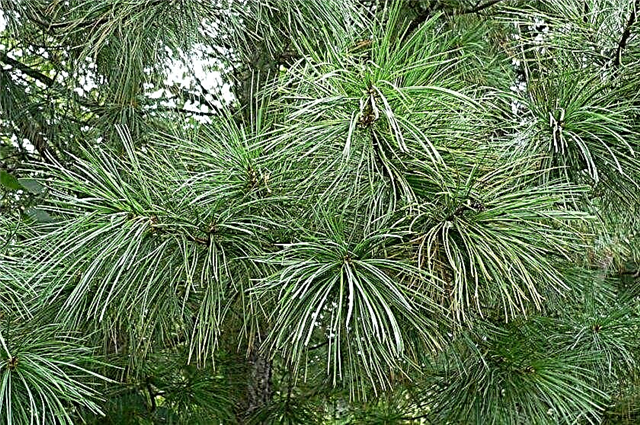

- Siberian pine. It is mainly found in the European part, namely in Eastern Siberia and in the north-eastern part of the region. The main cluster is observed in the Eurasian taiga.
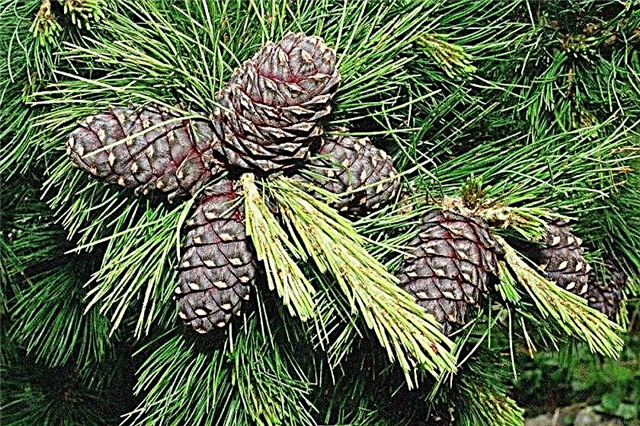

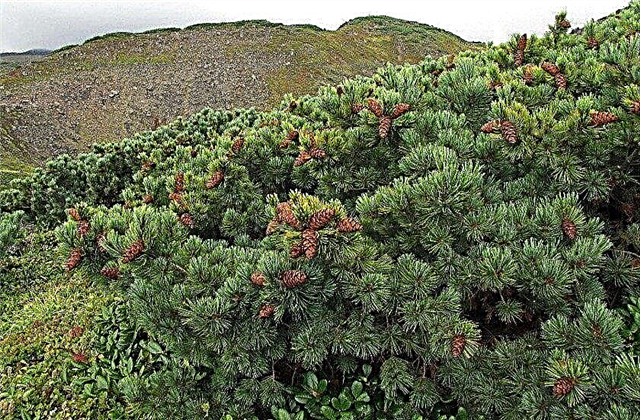
- Cedar elfin. This is one of the closest relatives of Siberian pine, which is a shrub of a stunted type. And it grows from the northern part of Eurasia up to the Arctic Circle, and mainly on the mountain slopes and plains, occasionally in Chukotka (in the regions of the circumpolar circle), in the Khabarovsk Territory (along the southern border). The cones are compact in size, and the nuts themselves are not so oily. The fruiting period begins after 20 years of growth, and formations form after 3 years until the plant reaches an age of about 200 years.

Cedar nuts usually begin harvesting in the first half of September. But the exact dates are always determined by the weather conditions of the summer season, during which the ripening period falls. The optimum time for ripening and subsequent easy shedding of cones is summer with high humidity. If there was a drought, then the fruits will be firmly fixed on the branch by means of resin, which means that they will fall off badly.
Did you know? Pinus Sylvestris is the oldest pine tree in the world. Her age is about 4800 years.
Killing seeds that are not ripe is prohibited. This harms the food supply of birds and animals living in the area. Late harvest is always limited to the hunting season. When the first snow falls, the harvesting of nuts is considered finished, and usually this is the end of October. In spring, nuts are harvested from April to May, and pay attention to the fallen fruits. This leads to the fact that the effectiveness of spring harvesting is much lower.
In which zone does cedar grow
The distribution area of cedar is a forest zone, in particular, in Russia. The tree is found mainly in group plantings, that is, it forms entire forests. The latter are often called dark coniferous taiga. In the northern part, cedar usually grows at low altitudes - 100–200 m. But in the south it grows at an altitude of 1000–2400 m. The plant is resistant to frost to -60 ° C.
Why cedars do not grow in Belarus
In Belarus, Siberian pine practically does not grow, so it will not work to find cones. The main reason is inappropriate soil, namely its acidity. The second factor is a higher air temperature in comparison with Siberia, the native place of cedar growth. In fact, pine needs moisture and snow for normal growth, which is not enough on the Belarusian lands.
Did you know? The easiest way to clean pine nuts from shells is to soak them in mineral or simply filtered water for 0.5–1 days. This leads to the fact that the fruits swell, the peel becomes soft, and you can even split it with your fingers.
There are exceptions when cedar pine is grown forcibly in special, almost greenhouse conditions. To do this, take a young seedling, for which they create a special soil, the required acidity and sprinkled with sawdust on top. The plant is regularly watered, as overdrying is very dangerous. Moreover, in the first year of life, the tree needs a shadow, weeding weeds. But in this case, you need to prepare for a very slow growth - a plant will grow literally by 50 cm in the first 5 years, but then things will go faster. Pine nuts grow almost all over the world, as evidenced by the developed botanical maps with marks of the places of growth of these evergreens. There are also some other types of pines that have seeds suitable for consumption.
Pine nuts grow almost all over the world, as evidenced by the developed botanical maps with marks of the places of growth of these evergreens. There are also some other types of pines that have seeds suitable for consumption.
But the fruits of the Siberian pine are considered the best in terms of energy value and chemical composition. It is worth noting the seeds of cedar dwarf, which are also good in the content of all kinds of active substances, but slightly inferior in the concentration of healthy fats.