To determine what type of hydrangea is better to choose for planting, you need to be able to distinguish between them. Each of these species can be grown both on personal plots and in city parks, because they are all undemanding to the quality of the soil and it is enough to simply look after them. But there are differences between these plants.
The differences between hydrangeas
Characteristics by which different types of hydrangeas differ from each other are very important, because only knowing them, you can decide to plant a particular plant.
First of all, you need to pay attention to winter hardiness, as well as the attitude of the species representative to lighting, watering and pruning. The color of the inflorescences and the height of the bushes are also of great importance if you want to create unique floral arrangements in your garden.
Important! In order not to buy a room hydrangea instead of garden hydrangea, you need to remember: at the “home”, unlike a street plant, the color of the inflorescences is much brighter.
Treelike and large-leaved
These two species are very different from each other, even in external characteristics. If the tree is a shrub, the height of which sometimes reaches 3 meters, then the large-leaved rarely grows to a meter.
Tree hydrangea blooms from June to September with large spherical or flat inflorescences, the color of which varies from pale green to white or cream. Sometimes flowers in inflorescences can be painted in pink tones, but such varieties are rare.

And here leaf hydrangea boasts the largest variety of shades, shapes and sizes of flowers in spherical inflorescences. Petals can be white, pink, red, purple, are also blue and blue, purple and raspberry.
Did you know? 95% of all hydrangeas in the world are grown in Holland.
There are specially bred chameleon varieties that change color during the flowering period. Flowers can be simple and multi-layered, double at the edges, round or slightly elongated.
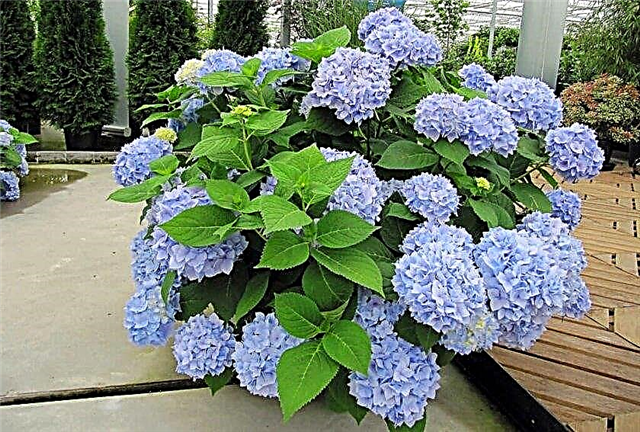

Treelike and large-leaved hydrangeas also differ in their leaves. In both species they are quite large and wide, but if the former has rough leaves, the latter is smooth and shiny. When planting these species, the fact that large-leaved, unlike others, very poorly tolerates wintering. For her, lowering the temperature even to -18 ° C can be fatal.
And here tree-like varieties are quite winter-resistant, therefore suitable even for terrain with a very harsh climate. Moreover this species blooms on young shootsthat develop from the lateral buds of old branches, so that their freezing in winter and early spring does not affect the presence and abundance of flowering.
And here large-leaved varieties form buds only on last year's shoots. Inflorescences are formed from the upper buds, so their slightest freezing can lead to a lack of flowering. For the same reason they are forbidden to cut, because in this case the bushes will bloom only next year.
And here tree hydrangea is very responsive to pruning and bush formation. If you do not prune its shoots, it can adversely affect the quality of flowering. In the spring, it is recommended to remove a little more than half of each shoot, as well as cut all the old branches, leaving only the youngest and strongest.
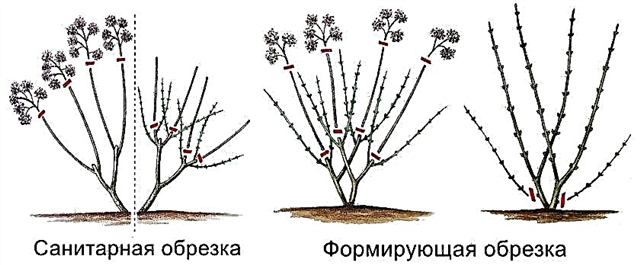
Treelike hydrangea can endure short-term drought, and large-leaved hydrangea is very demanding on moistening the soil, and also burns very much if it is under direct sunlight, therefore, it needs shelter or the creation of a small partial shade.
Panicled and tree-like
These types of hydrangeas are very similar to each other. They differ only in the form of inflorescences and coloring features. In panicled flowers, they are collected in “panicles” with a length of about 15–25 cm, less often there are spherical. And the variety of colors they have is richer than that of tree-like varieties. There are lemon, yellow, pink, and closer to the end of flowering, they become purple, raspberry.
A feature of some varieties of panicled hydrangea is a very effective wilting. Dry flowers retain a bright purple color. To the touch, the petals resemble parchment paper. therefore they are often used to create original floral arrangements of dried flowers.
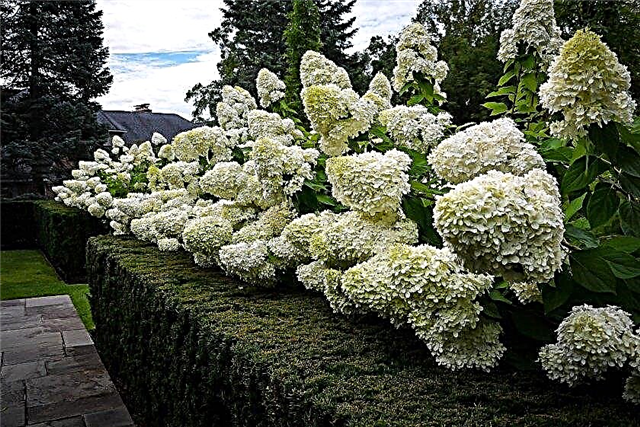

The leaves and shoots of these plant species are also different. The leaves of the tree are large and rough to the touch, while the paniculate leaves are small, bright green, and in the fall they become purple or burgundy. The shoots of the varieties of this species also have a burgundy color, which is their distinguishing feature.
Attitude to pruning and watering, as well as resistance to lowering temperature in these varieties is identical. Plants of the described species tolerate wintering quite well and need shaping and anti-aging pruningwhich are very important for high-quality and plentiful flowering.
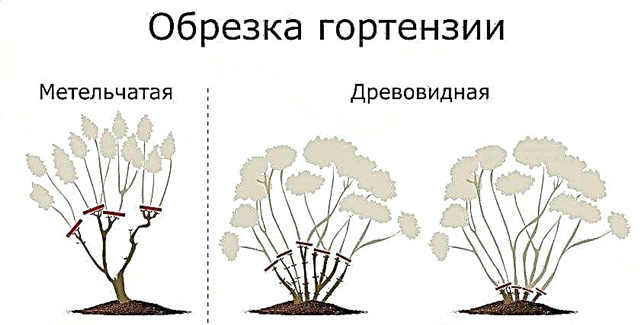 Inflorescences in both species are formed on young shoots, so neither shortening nor freezing can affect them.
Inflorescences in both species are formed on young shoots, so neither shortening nor freezing can affect them.
As already noted, tree hydrangea can remain without watering for some time, but panicled hydration should be moistened regularly, and not only water it, but also spray the crown with water.
Panicled hydrangea also has such a feature - its flowers smell very nice. And also a plant of this species, if desired, can be formed by a tree with a lush crown, removing all shoots and leaving only the central one.
Leafy and panicled
Large-leaved and panicled hydrangeas differ in the form of inflorescences, the size of the leaves, as well as the richness of colors. In addition, they have many differences in care, especially in their relation to lowering the temperature.
Panicled hydrangea tolerates wintering well, especially if it is covered with soil or covered, but large-leaved leaves often freeze even with cover.

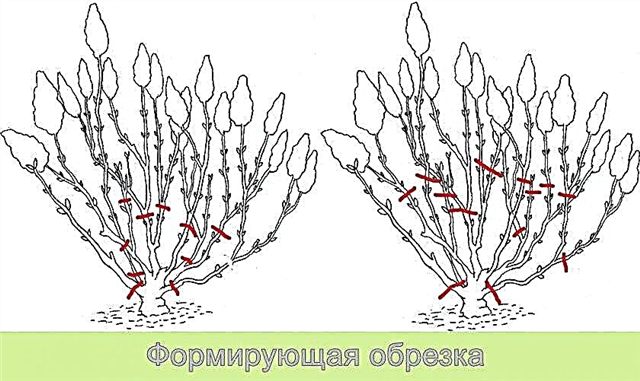
Due to the fact that large-leaved varieties bloom only on last year's shoots, or rather, on their green shoots emerging from the apical buds, they should in no case be subjected to freezing and pruning. Because of this, breeders are now breeding repairing varieties that can bloom on both young and old shoots, because even in case of freezing they will be able to bloom, but only closer to fall.
Panicled hydrangea does not have such problems, because inflorescences on its bushes are formed on the shoots of the current year. Large-leaf varieties cannot be cut, and in no case do they pinch off the tops on which the buds are located, forming inflorescences next year.
And here panicled hydrangea is very responsive to crown formation, therefore, it can be cut in the form of a bush, and in the form of a tree, which is a distinctive feature of this species. And it, unlike large-leaved hydrangea, is much higher, and can grow up to 3 meters.
Which hydrangea is better
The choice depends on the conditions under which you plan to grow the plant, and what characteristics are more important to you.
Choosing one of the tree varieties is worth in such cases:
- if you live in a rather harsh climate with cold winters;
- when it is not possible to water the bushes very often;
- when you need tall plants to create beautiful decorative compositions.
Important! When choosing the right variety of hydrangea, you must definitely find out what temperature drops it can tolerate so as not to lose bushes or potential flowering in the next season due to severe frost.
Panicled varieties will be appropriate in situations:
- if you want to plant a beautiful, but unpretentious plant care;
- in case you are more interested in trees than shrubs;
- when not only the beauty of inflorescences is important for you, but also their aroma;
- if you choose a variety with good resistance to low temperatures.
But large-leaved hydrangea will appeal to fans of unusual colors and shapes, and it can also be grown in pots due to its low growth and compactness.
It is not difficult to distinguish different types of hydrangea if you know their main characteristics. Paniculate and tree-like are similar to each other, but with the large-leafed, they have a significant enough difference. And the choice of a plant depends on the place in which it will grow, and also on what care measures it requires.